Hydrogen And Its Compounds









Hydrogen And Its Compounds
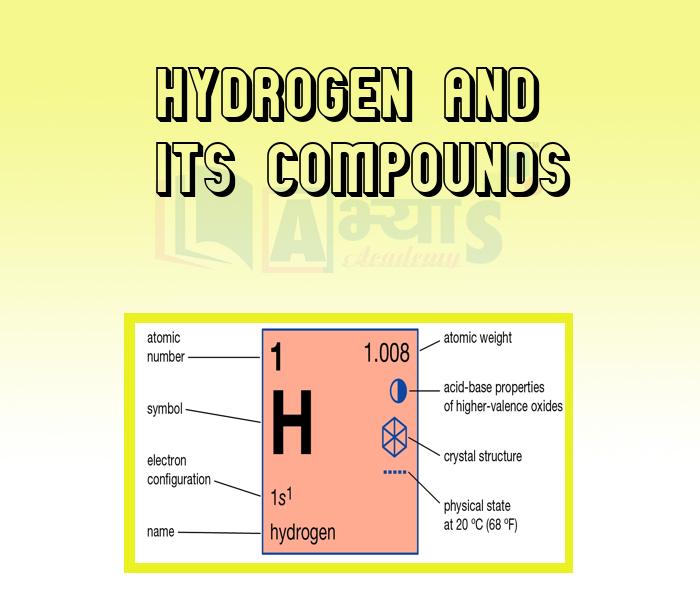
Hydrogen: Hydrogen (atomic number 1; atomic weight 1.00797) is the first chemical element in the periodic system. Under ordinary conditions, it is a colourless, odourless, tasteless gas composed of diatomic molecules, H. It is a major constituent of water and all the organic matter and is widely distributed throughout the universe.
At ordinary temperatures, hydrogen is comparatively non-reactive but at elevated temperatures. It is highly reactive, It reacts with oxygen to form water. With nitrogen, it undergoes an important reaction to give ammonia. Large quantities of hydrogen are consumed in the catalytic hydrogenation of unsaturated liquid vegetable oils to make solid fats, Hydrogen is also used as a rocket fuel in combination with oxygen or fluorine.
Compounds Of Hydrogen:
Water: Water is probably the most abundant as well as the most important compound upon the earth. Water is essential to all forms of life. It is the most abundant compound in the biosphere. Of the total estimated global water supply, the oceans and inland saline water bodies have 97.3% and fresh water amounts to only 2.7%. Unfortunately, most of the fresh water is not readily accessible, being locked up in frozen lakes, glaciers or under the ground. The fraction of water available for human use is only 0.003% of the total global water supply. In nature water is found in all three phases - solid, liquid, and gas. Molecular Structure Water has the chemical formula .
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
Being a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.
